

Using this data source, we can create a table based on customer name and total balance. Open a new workbook in tableau desktop and connect the data sources using the.
#Statistical calculations calcualtor download#
Steps to download Tableau Desktop: Click hereĭownload Bank Customer Dataset: Click here
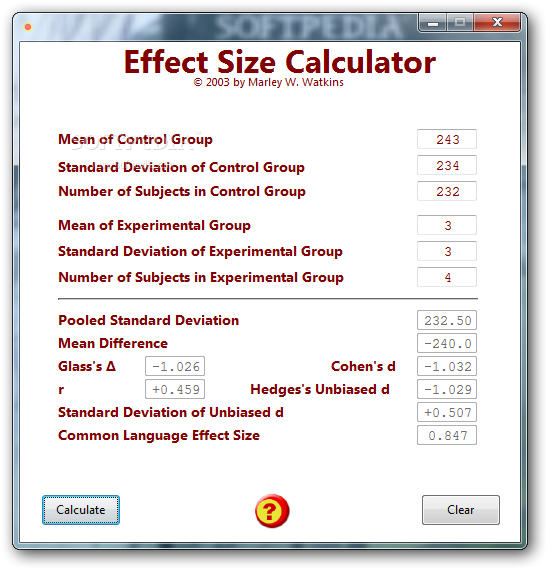
Variances (the standard deviation is the square root of variance) can be added. Statistical Stack-upĪ widely used method for performing a statistical stack-up analysis is the root-sum-squares (RSS) method. 99.7% of the population falls within the +/-3σ limits. To remind (?) you: the standard deviation is a measure for the variation. An additional benefit is that adding up normal distributed tolerances is relatively easy.Īn assumption that is often made is that the tolerance limits coincide with the +/-3σ (3x standard deviation) values. Because the production process of machined parts consists of a lot of variables, a normal distribution of tolerances is safe to assume. Roughly speaking, this theorem says that “the sum of a large number of small and independent random variables will be approximately normally distributed”. In statistics this is called the central limit theorem. This is because the normal distribution seems to arise in ‘almost all cases’. Often it is assumed that tolerances have a normal (Gaussian) distribution. If you don’t know the distribution of tolerances, you have to make an estimation. But what if you’re working on a new product and you don’t have this kind of data for comparison at hand? Normal Distribution of Tolerances When similar parts have been produced already, you have important data at hand to make a good estimation of the tolerance distribution. That question is not that easy to answer but a better estimate would increase the accuracy of your analysis. The question now is what a (more) realistic distribution is. In the worst-case example above there was an extreme distribution of tolerances. It is clear that it is beneficial to take the probability distribution of tolerances into account and perform a statistical analysis. In practice the probability of an extreme height is very low. Notice that this is an extreme distribution of tolerances with a low probability itself.
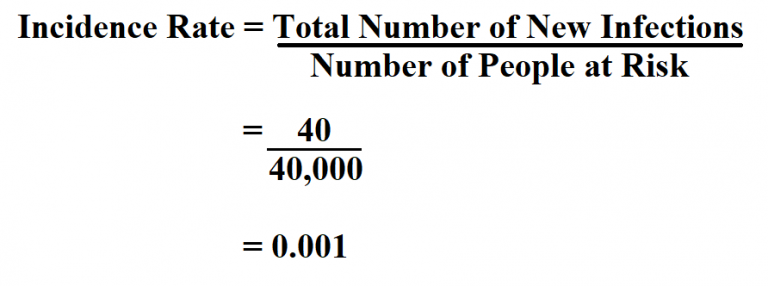
If for instance only the highest stack is problematic than this probability is only 6.25%. The probability of an extreme thickness is 2/16 = 12.5%. With just 4 parts it is still doable to write down all possible combinations. The parts have a height of 10 +/-1 and are either 9 ( part ‘9’) or 11 ( part ’11’). Suppose that you make a stack of 4 identical parts and you want to analyze the total height of the stack. It turns out that the probability of a worst-case combination is negligible for already a small number of parts. In a statistical analysis the probability of a tolerance value and the combination of tolerances is taken into account. In such an analysis it is assumed that all dimensions in the tolerance chain have worst-case deviations form their nominal value. In the article Worst-case Tolerance Stack-up Analysis you read about the worst-case or linear stack-up analysis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
